Bootstrap
Lecture 20
Dr. Elijah Meyer + Konnie Huang
Duke University
STA 199 - Fall 2022
November 7th, 2022
Checklist
– Clone ae-19
Announcements
– Project Proposal (Due tonight: 11:59)
– Peer Review due tonight
– Office Hour Change: 1-3 Tuesday
Peer Review Purpose
– Open Communication
– If there is a serious issue that you would not like to share with your team, please reach out.
Project Proposal
Introduction and data: motivation and context for your research.
Methodology: include visualizations and summary statistics relevant to your research question. You should also justify the choice of statistical method(s) used to answer your research question.
Results: Provide only the main results from your analysis.
Abstract: An abstract is a concise summary of a research paper / project. An abstract lets readers get the gist or essence of your paper or article quickly. Search for a research paper to get the gist of it (https://scholar.google.com/).
Hints
– Reference the AEs and Videos for example research questions
– Write yourself a project outline
What is the topic?
Why do we care?
What are we interested in?
– Introduction
present relevant background or contextual material
define terms or concepts when necessary
explain the focus of the paper
reveal your plan
Project Proposal
Your next project related deadline is Mon, Nov 7 at 11:59pm. Your project draft, written in report.qmd, must be pushed to GitHub by that time. You will lose push access to your repo at that time until your draft has been reviewed.
You will receive feedback as issues on your GitHub repository.
Issues
Goals
– Simple & Multiple Linear Regression vs Logistic Regression
– What is bootstrapping
– What is a confidence interval
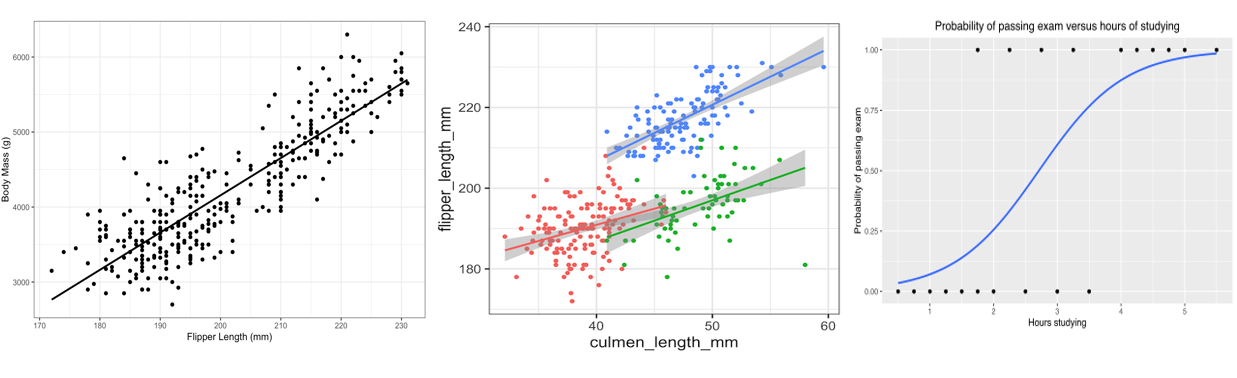
Types of Regression (SLR, MLR, Logistic)
– What types of variable is the response?
– What types of variable(s) are the explanatory?
– Number of explanatory variables?
– Linear Regression or Generalized Linear Regression?
This week
– Is all about concepts
– Main goal is to develop a fundamental understanding about bootstrapping, confidence intervals, and hypothesis testing. We will put our understanding into more practice starting next week.
ae-19 - Bootstrap
In Summary
Bootstrap methods are simulation methods
Variability - Uncertainty: How spread out your data are
We can use this to guess plausible values around our parameter of interest
This is called a confidence interval, and it’s different than probability
