Multiple Predictors
Lecture 18
Dr. Elijah Meyer + Konnie Huang
Duke University
STA 199 - Fall 2022
October 31st, 2022
Checklist
– Clone ae-17
– If you do not have ae-17 go here: https://github.com/sta199-f22-2/ae-17

Announcements
– Lab Feedback (Check it regardless of your grade)
– HW4 Question 2
Goals
– Overfitting
– “New” function in R
Summary on Regression
– Why we model data?
– Can I write out models?
– Can I interpret model output?
– Do I understand the difference between models?
Warm Up
Discuss the difference between the two models below. Which model would you prefer to fit to model these data? Why?
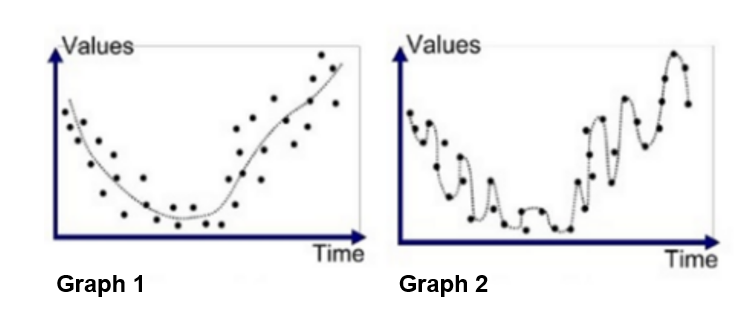
Overfitting
– Overfitting is a concept in data science, which occurs when a statistical model fits exactly against its data.
– This doesn’t make sense if are goal is to predict!
Why we use regression
Predict the value of our response
Estimate the effect of some explanatory variable on the response (examine the relationship)
Make inference about some larger population (coming later)
When and why we use regression
Quantitative Response
Does it make sense
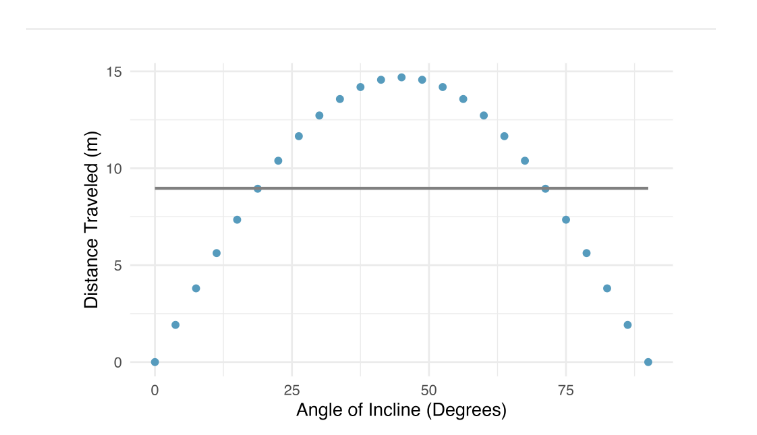
Extension (Coming Later)
To test hypotheses and make conclusions, certain assumptions need to be met….
– Normality of Residuals
– Linearity
– Independence
– Constant Variance
Jump into ae-17
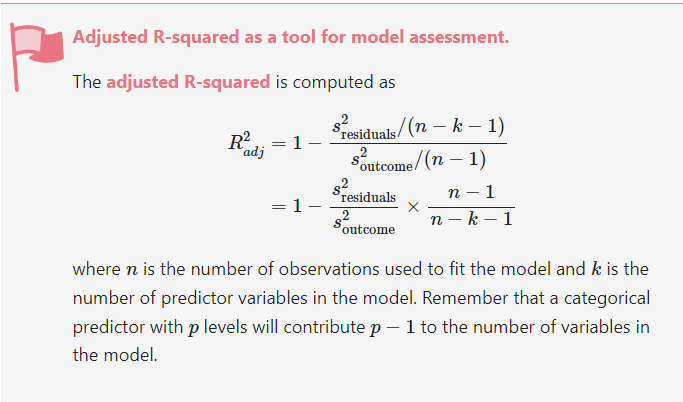
Adjusted R-squared
Modeling More Than One Variable
– Multiple linear regression is used to estimate the relationship between two or more explanatory variables and one response variable.
– we want to predict the value of a variable based on the value of two or more other variables
– “account for X1 and assess the relationship between X2 and Y” - main effects
– “does X1’s relationship with Y change based on X2”
Logistic Regression
– What if the response variable is categorical?
