Exam Review
Lecture 10
Dr. Elijah Meyer + Konnie Huang
Duke University
STA 199 - Fall 2022
September 28, 2022
Checklist
– Clone exam review repo
– Prepare for exam 1
Exam Logistics
– This is an individual exam (No Slack / No TAs / No Instructor)
– Clarification questions are welcome. Debuging is not:
What’s a tiny bit of help vs. what’s help to get unstuck
There would be no equivalent to this in an in person exam
If a student truly is stuck because of a reason not in their control, we wouldn’t penalize them anyway
– Turn in via PDF. If you fail to do so, we will grade your latest commit and issue a penalty
– Cite any code you obtain outside of the course materials
– Look at what’s rendered!
Office Hours
– Friday 10:00 - 11:00AM
Goals
– Pivots
– Joins
– Relationship Discussion
– Data wrangling with dplyr
Warm up
Suppose you and another researcher collected data on coffee separately. You collect the data on the left, and they collect the data on the right. Based on the question asked, identify the appropriate join function to join these two data together.

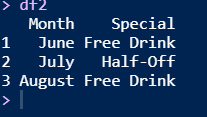
– Add a column to your data set called special to indicate which months had speical drink offers.
– Add a column to your data set called special to indicate which months had speical drink offers. Only include months in your data set that had specials.
left_join
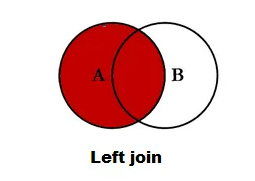
inner_join

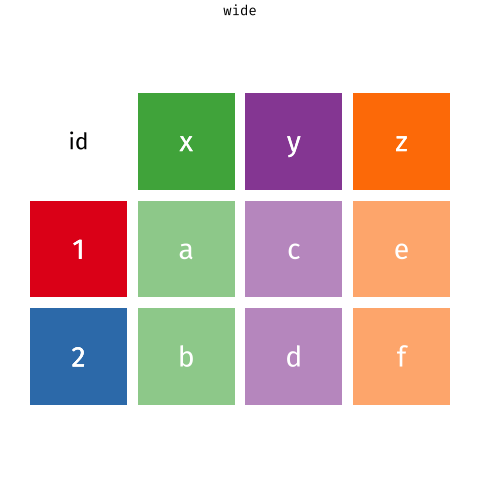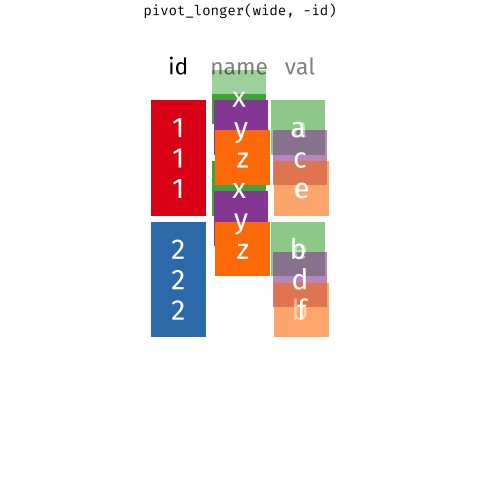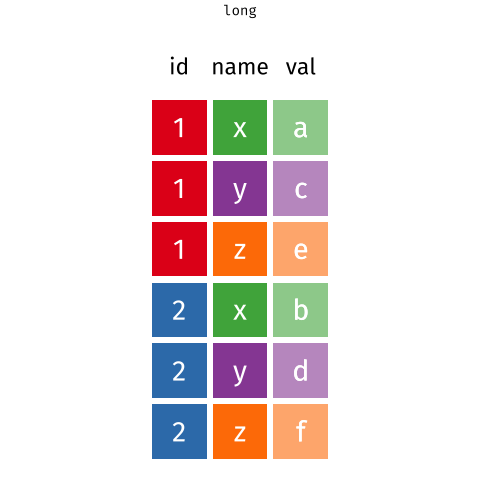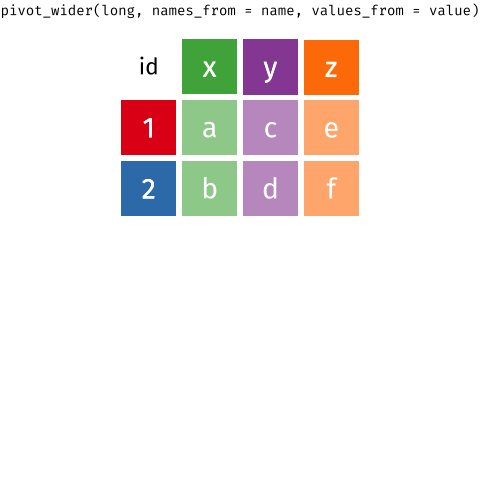
Pivot Wider and Longer
With a wide structure, each person (observational unit) has one observation (row) and a separate column contains data for each measurement. With a long structure, each person (observational unit) has multiple observations; one measurement per row.
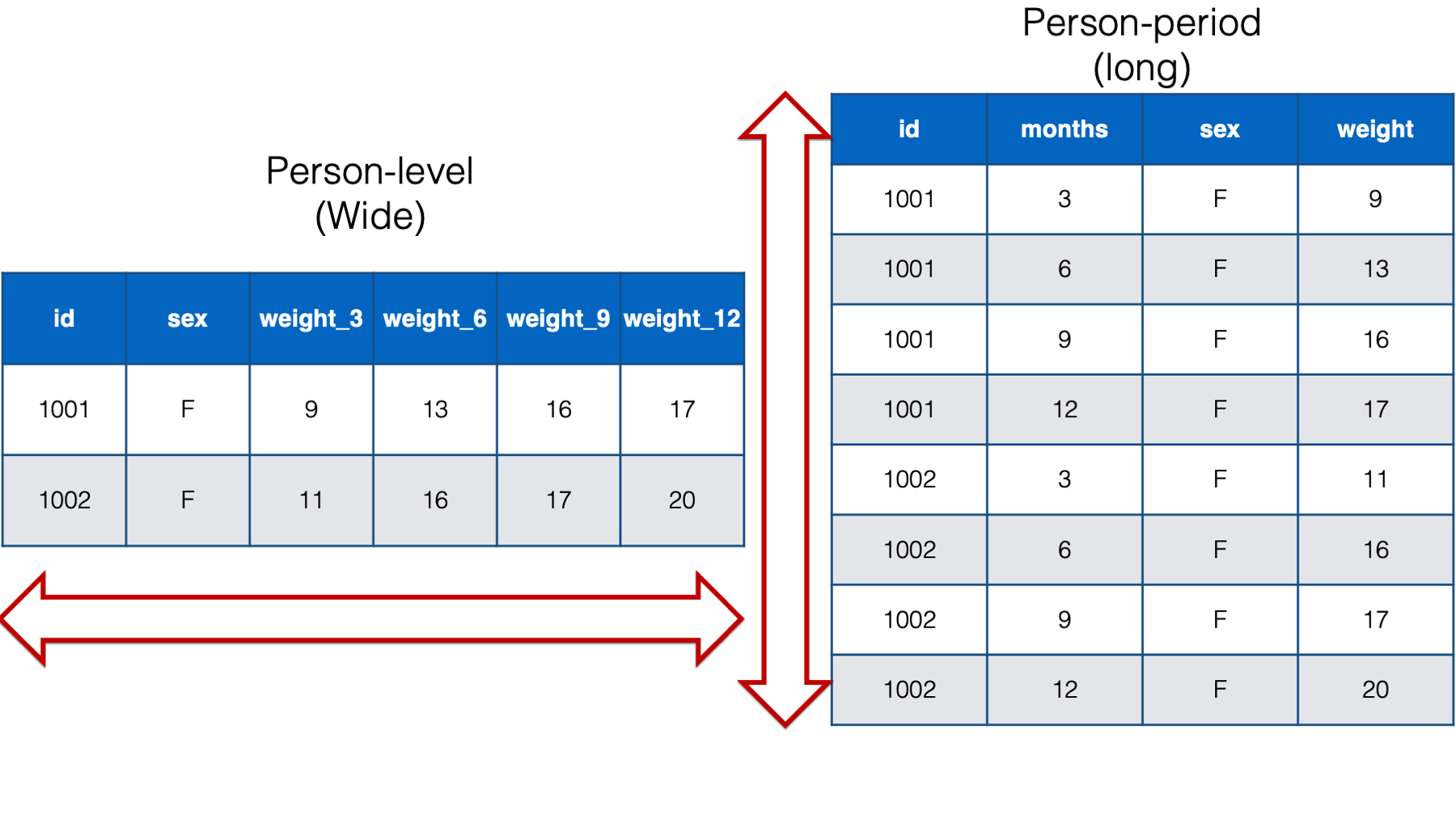
The data
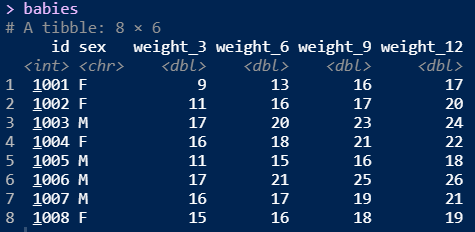
The code

babies <- babies |>
pivot_longer(
cols = -c(“id”, “sex”),
names_to = “months”,
names_prefix = “weight_”,
values_to = “weight”
)
The code - answers
– The second argument to the pivot_longer() function is the cols argument. You should pass the name of the columns you want to make longer to the cols argument.
– The third argument to the pivot_longer() function is the names_to argument. You should pass the names_to argument a character string or character vector that tells pivot_longer() what you want to name the column that will contain the previous column names that were pivoted.
– The fourth argument to the pivot_longer() function is the names_prefix argument. You should pass the names_prefix argument a regular expression that tells pivot_longer() what to remove from the start of each of the previous column names that we pivoted.
– The eighth argument (we left the 5th, 6th, and 7th arguments at their default values) to the pivot_longer() function is the values_to argument. You should pass the values_to argument a character string or character vector that tells pivot_longer() what you want to name the column that will contain the values from the columns that were pivoted.
In action
 {Long to Wide + Wide to Long}
{Long to Wide + Wide to Long}
long data to wide
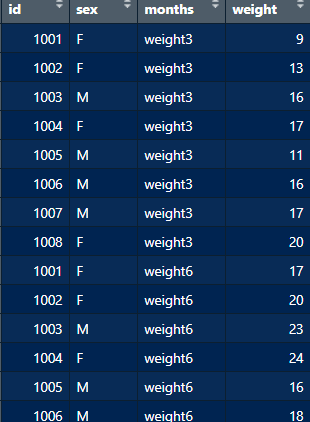
pivot-wider
babies <- babies_long |>
pivot_wider(
names_from = “months”,
values_from = “weight)
)
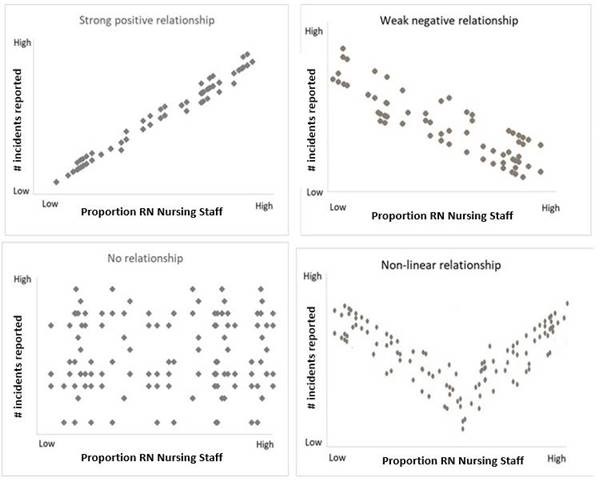
Relationships
How we talk about graphs….
Scatterplot
Interactions
Boxplot
Barplot